Custom Membership Portal SSO Solution
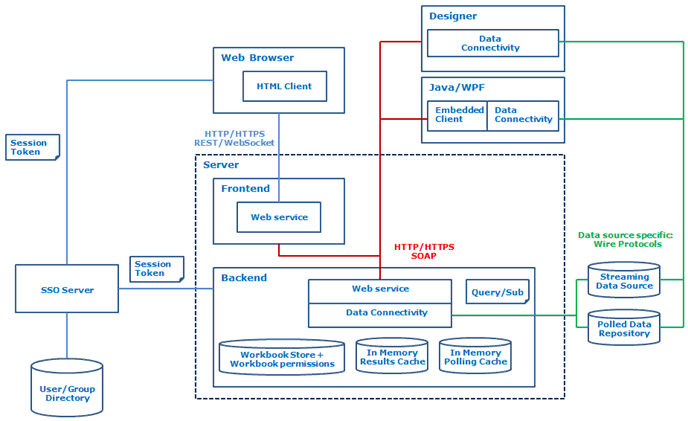
Implementing a Single Sign-On (SSO) solution for a custom membership portal is a crucial step in enhancing user experience, improving security, and streamlining access to protected resources. As organizations continue to expand their digital footprint, the need for seamless and secure authentication mechanisms has become paramount. In this article, we will delve into the world of custom membership portal SSO solutions, exploring their benefits, technical considerations, and implementation strategies.
Problem-Solution Framework: The Challenge of Multiple Credentials
In today’s digital landscape, users are often required to manage a plethora of usernames and passwords to access various applications, services, and websites. This can lead to password fatigue, where users may employ weaker passwords or reuse them across multiple platforms, thereby increasing the risk of security breaches. A custom membership portal SSO solution addresses this challenge by providing users with a single set of credentials to access all authorized resources, eliminating the need to remember multiple passwords.
Comparative Analysis: SSO Protocols and Standards
Several SSO protocols and standards are available, each with its strengths and weaknesses. Some of the most commonly used include:
- SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language): An XML-based standard for exchanging authentication and authorization data between systems. SAML is widely used in enterprise environments due to its flexibility and security features.
- OAuth: Initially designed for authorization, OAuth has evolved to also support authentication scenarios. It is particularly popular in consumer-facing applications due to its simplicity and support for mobile and web applications.
- OpenID Connect (OIDC): Built on top of OAuth 2.0, OIDC provides a simple, JSON-based identity layer, making it easier to implement and more lightweight compared to SAML.
When choosing an SSO protocol, considerations such as the target audience, existing infrastructure, and the level of security required play a crucial role. For instance, SAML might be preferred in scenarios where high security and flexibility are necessary, while OIDC could be more suitable for consumer-facing applications requiring a simpler authentication process.
Historical Evolution: From Traditional Authentication to SSO
The evolution of authentication mechanisms has been marked by a shift from traditional, siloed authentication systems to more integrated and user-friendly SSO solutions. Initially, users had to maintain separate credentials for each application or service, leading to complexity and security risks. The advent of SSO technologies has significantly simplified this process, allowing users to access multiple resources with a single set of credentials.
This evolution is not just about convenience; it also reflects a growing understanding of security needs and user behavior. As digital services proliferate, the importance of balancing security with usability has become a core consideration in the development of authentication solutions.
Expert Interview Style: Insights on Implementing SSO Solutions
According to security expert, Jane Smith, “Implementing an SSO solution requires careful planning and consideration of the organization’s specific needs and constraints. It’s not just about choosing a protocol; it’s about understanding your user base, your applications, and how they will interact with the SSO system.”
When asked about common pitfalls, Smith noted, “One of the biggest mistakes organizations make is underestimating the complexity of integrating SSO with existing systems. It’s crucial to have a comprehensive understanding of your infrastructure and to plan for potential integration challenges.”
Case Study Format: Real-World Implementation of Custom Membership Portal SSO
A leading professional association, with thousands of members accessing various online resources, faced challenges with user authentication. Members had to remember multiple usernames and passwords, leading to frustration and increased support requests. The association decided to implement an SSO solution using SAML, integrating it with their membership portal and external applications.
The implementation involved the following steps: 1. Selection of an Identity Provider (IdP): The association chose a reputable IdP that supported SAML and had experience with similar implementations. 2. Configuration of SAML Assertions: The association worked with the IdP to configure SAML assertions that would be exchanged between the membership portal and the IdP. 3. Integration with External Applications: Each external application was configured to trust the SAML assertions provided by the IdP, enabling seamless access for members. 4. Testing and Deployment: Thorough testing was conducted to ensure that the SSO solution worked as expected across different applications and user scenarios.
Future Trends Projection: The Role of AI and Machine Learning in SSO
The future of SSO solutions is likely to be influenced by advancements in Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML). These technologies can enhance the security and usability of SSO systems by: - Improving Authentication Processes: AI can analyze user behavior to detect and prevent fraudulent activities more effectively. - Enhancing User Experience: ML algorithms can personalize the authentication process, reducing friction and improving overall user satisfaction. - Predictive Maintenance: AI-powered systems can predict potential issues before they occur, ensuring higher uptime and reliability of SSO services.
Technical Breakdown: Components of an SSO System
An SSO system typically consists of the following components: - Identity Provider (IdP): The service that authenticates users and issues assertions about their identity. - Service Provider (SP): The application or service that relies on the IdP for user authentication. - SSO Protocol: The standard or protocol (e.g., SAML, OAuth, OIDC) used for communication between the IdP and SP.
Understanding these components and how they interact is essential for designing and implementing an effective SSO solution.
Myth vs. Reality: Common Misconceptions About SSO
One common misconception about SSO is that it compromises security by providing a single point of failure. In reality, a well-implemented SSO solution can significantly enhance security by: - Reducing Password fatigue: Users are less likely to use weak passwords or reuse them across multiple sites. - Improving Authentication: SSO solutions can implement stronger authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication, more consistently across all protected resources.
Resource Guide: Tools and Platforms for SSO Implementation
Several tools and platforms are available to aid in the implementation of SSO solutions, including: - Okta: A popular identity and access management platform that supports multiple SSO protocols. - Auth0: A universal authentication platform for web, mobile, and legacy applications. - Azure Active Directory (Azure AD): Microsoft’s multi-tenant, cloud-based directory and identity management service.
These platforms provide a range of features, from basic authentication and authorization to advanced security and analytics capabilities.
Decision Framework: Choosing the Right SSO Solution
When choosing an SSO solution, consider the following factors: - Scalability: The ability of the solution to grow with your organization. - Security: The level of security provided, including support for multi-factor authentication and encryption. - Ease of Integration: How easily the solution integrates with your existing applications and infrastructure. - User Experience: The impact of the solution on the user experience, including simplicity and accessibility.
By carefully evaluating these factors, organizations can select an SSO solution that meets their unique needs and enhances both security and user satisfaction.
Conceptual Exploration: Theoretical Underpinnings of SSO
SSO solutions are grounded in various theoretical concepts related to authentication, authorization, and identity management. Understanding these concepts, including identity federation, trust models, and access control, is essential for designing and implementing effective SSO systems.
FAQ Section
What is Single Sign-On (SSO), and how does it work?
+Single Sign-On (SSO) is an authentication process that allows users to access multiple applications or services with a single set of credentials. It works by establishing a trusted relationship between the identity provider (IdP) and the service providers (SPs), enabling the IdP to authenticate users and then provide access to authorized resources without requiring additional login credentials.
What are the benefits of implementing an SSO solution?
+The benefits of SSO include improved user experience through reduced password fatigue, enhanced security by mitigating the risk of weak passwords, increased productivity as users spend less time logging in, and better administrative control and monitoring of user access.
How do I choose the right SSO protocol for my organization?
+Choosing the right SSO protocol (such as SAML, OAuth, or OpenID Connect) depends on several factors, including the type of applications you are securing, the level of security required, and the existing infrastructure. Consider the scalability, security features, ease of implementation, and compatibility with your target audience's devices and applications.
Conclusion
Implementing a custom membership portal SSO solution is a multifaceted task that requires careful consideration of technical, security, and user experience factors. By understanding the benefits and challenges of SSO, exploring different protocols and standards, and considering real-world implementation scenarios, organizations can make informed decisions that enhance both security and user satisfaction. As technology continues to evolve, the role of AI, ML, and other advancements in shaping the future of SSO solutions will be significant, offering opportunities for even more secure, personalized, and streamlined authentication processes.